Pertemuan ke 1- Data Structure - 2101724213- Kunta Rizki Purnama
There a some material that you should know, this material is based on introduction of Data Structure. There a Pointer, Array, and introduction to Data Structure.
•One Dimensional Array •Declaration: •int
arr[5];
•Two Dimensional Array
Syntax: type name[size1][size2]; •The
first index of array ranged from 0 to size1
– 1. •The
second index of array ranged from 0 to size2
– 1.
type ame[size1][size2][size3][...]; •The
first index of array ranged
Pointer is a
data type whose value refers to another value stored
•Supposed
we want to create an ADT of natural number which has integer number as objects
and several functions as operation.
- Array
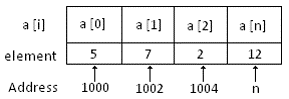
A collection of similar data elements, These data elements have the same data type (homogenous). The elements of the array are stored in consecutive memory locations and are referenced by an index. Array index starts from zero
- Array Declaration and Accessing Array
•One Dimensional Array •Declaration: •int
arr[5];
•Accessing: •arr[0]
= 7; •arr[1]
= 2; •arr[2]
= 13; •arr[3]
= 13; •arr[4]
= 13;
Syntax: type name[size]; An array of size N have indexes from 0 to N-1.
•Two Dimensional Array
•Declaration: •int
arr[3][6];
•Accessing: •arr[0][2]
= 2; •arr[2][1]
= 9; •arr[1][5]
= 13; •arr[2][4]
= 10;
Syntax: type name[size1][size2]; •The
first index of array ranged from 0 to size1
– 1. •The
second index of array ranged from 0 to size2
– 1.
•Multi Dimensional Array
•Declaration:
•int
arr[4][3][7][10];
•Accessing:
•arr[0][2][2][9]=
2;
•arr[2][1][6][0]=
9;
•arr[3][0][0][6]=
13;
•arr[2][1][3][8]=
10;
Syntax:
type ame[size1][size2][size3][...]; •The
first index of array ranged
from 0 to size1 – 1. •The
second index of array ranged
from 0 to size2 – 1. •The
third index of array ranged
from 0 to size3 – 1. •and
so on.
2. Pointer
Pointer is a
data type whose value refers to another value stored
elsewhere in computer memory using
its address.
The two most important operators
used with pointer type are: • & the address operator • * the
dereferencing operator
If we have the declaration:
int x; int *px;then x is an integer and px is a pointer to an integer. If we say: px = &x;then &x returns the address of x and assigns it as the value of px.To assign a value of x we can say x = 10;or *pi = 10;
What is the output of this program?•int a = 10;int *p = &a;printf( “%d\n”, *p );a
= 17;*p = 20;printf( “%d\n”, a );
3. Data Structure
•A data structure is an arrangement of data, either in the computer’s memory or on the disk storage.
•Some common examples of data structures include:–Arrays–Linked lists–Queues–Stacks–Binary trees–Hash tables
Types Of Data Structure
•Arrays
–A
collection of similar data elements
•Binary
Trees
–A
data structure which is defined as a collection of elements called the nodes
–Every
node contains a left pointer, a right pointer, and a data element
4. Abstract Data Type
Abstract
Data Type
(ADT) is a data type that is organized in such a way that the specification of
the objects and the specification of the operations on the objects is separated
from the representation of the objects and the implementation of the
operations. C/C++
has a concept called class and struct
which assist the programmer in implementing abstract data type.
Example Of ADT :
•Supposed
we want to create an ADT of natural number which has integer number as objects
and several functions as operation.
•structure
Number is objects : an integer x functions : bool
is_zero() if ( x == 0 ) return TRUE else
return FALSE bool
equal(y) if ( x == y ) return TRUE else
return FALSE void
set(y) x = y void
add(y) x = x + y int
get () return
x
Summary :
•Pointer is a data type whose value refers
to another value stored elsewhere in computer memory using its address
•Array
is a collection
of similar data elements
•Array index starts from zero
•A
data structure is an arrangement of data, either in the computer’s memory or on
the disk storage
•Some
common examples of data structures include: arrays, linked lists, queues,
stacks, binary trees, hash tables
•Abstract Data Type (ADT) is a data type
that is organized in such a way that the specification of the objects and the
specification of the operations on the objects is separated from the
representation of the objects and the implementation of the operations
Reference :
•Reema Thareja,. 2014. Data
structures using C. OXFOR. New Delhi. ISBN:978-0-19-809930-7 Chapter 1 & 3
•Arrays in C/C++ Programming

Komentar
Posting Komentar